Houdini supports two types of volume primitive:
Standard Houdini volumes
A standard Houdini volume is a box with a position, size, and orientation, subdivided into a 3D grid of voxels, with a value stored in each voxel. This type is used in modeling (SOPs) and simulation (DOPs).
OpenVDB volumes
An OpenVDB volume uses the OpenVDB library to represent a sparse volume very efficiently. A VDB volume uses essentially no memory for “empty” voxels (technically, voxels equal to the “background value”).
For more information see https://www.sidefx.com/docs/houdini/model/volumes.html
Different types of volumes store different types of information in the voxels:
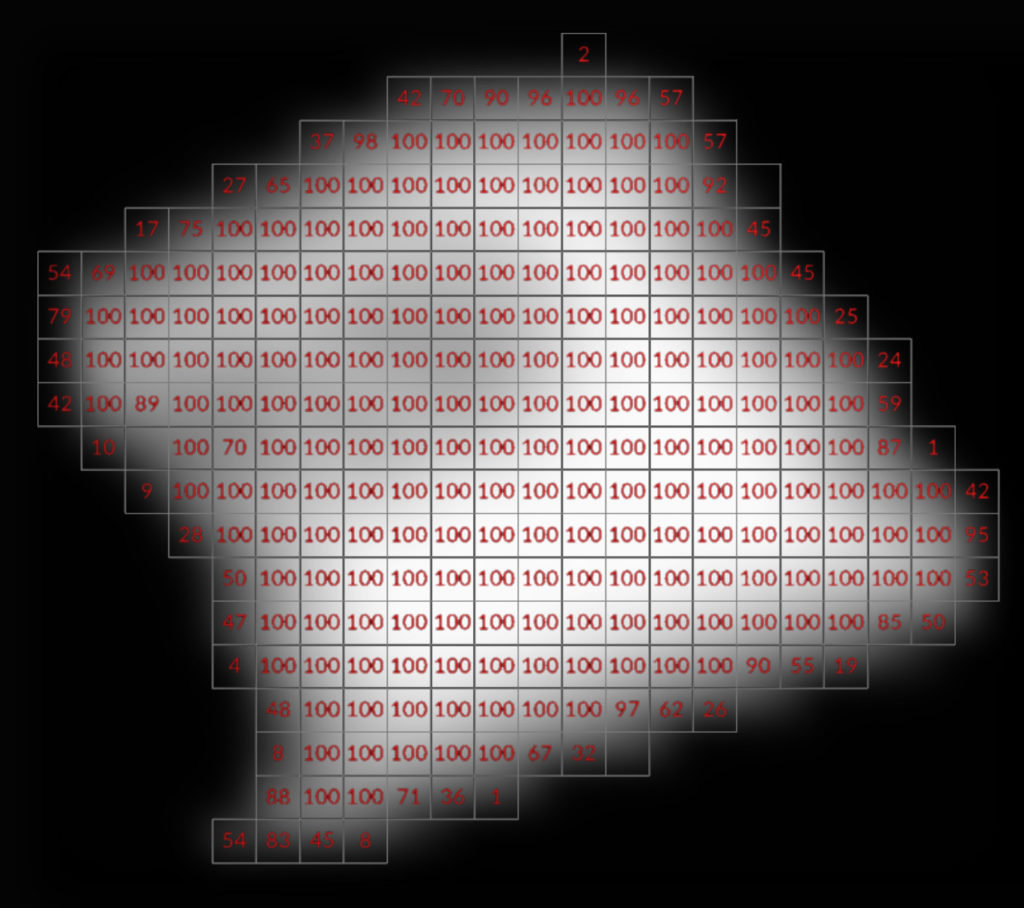
Fog Volume
has a density attribute which can represent the thickness of the fog but can be any value with any name, and can be a float or a vector. Vectors can be used to store direction/velocity of gases. Designed for gases.
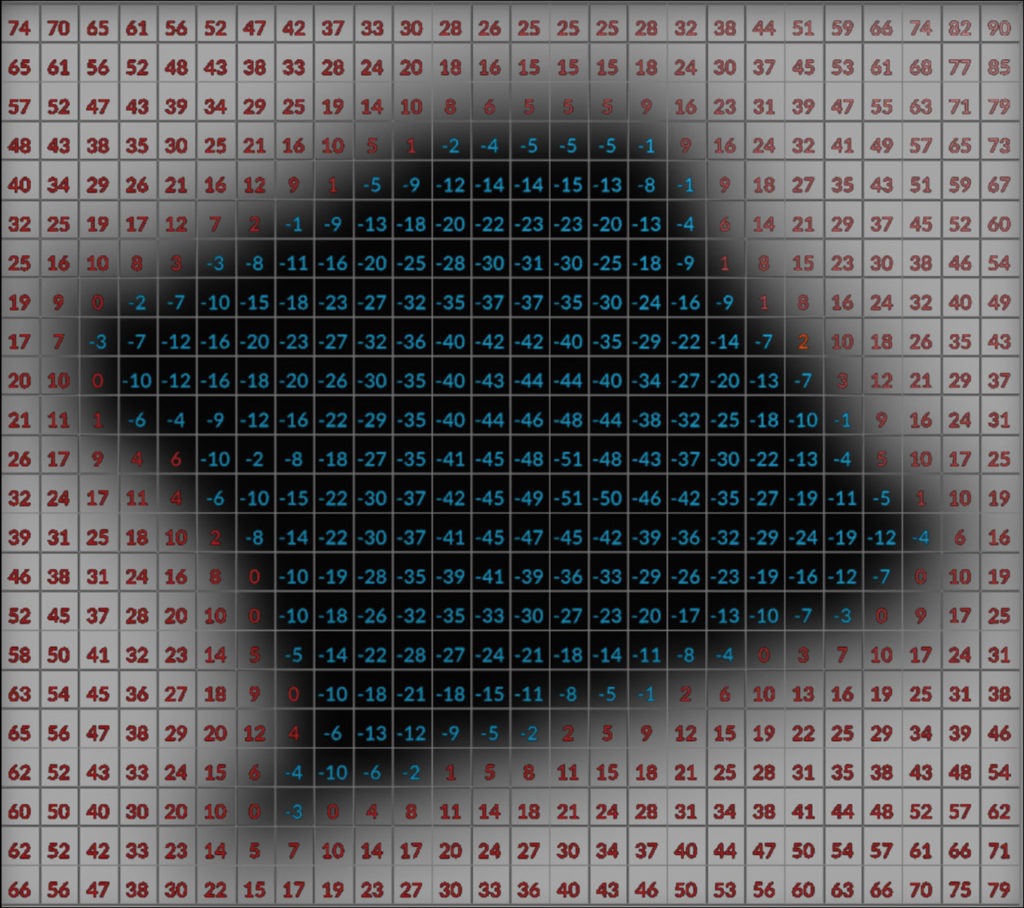
Signed Distance Field
Voxels inside the volume negative value that represents the distance inside the surface. Voxels outside have a positive value that represents the distance outside the surface. Designed for liquids.
Common uses for Volumes in procedural geometry, and how to achieve them